The business of Geomatics has undergone continuous evolution to get to where it is today. The tools and technologies used are far more sophisticated digitally than what was used in the past. While many now think of Geomatics as a mature and well established profession, the reality is it is still evolving, perhaps faster now than ever before. Over the past couple of decades, the business and science of Geomatics has collided with modern digital technology and information and is one of the largest sources of “Big Data” on engineering projects. It is through the production and delivery of these large volumes of highly precise and detailed geospatial information that Geomatics produces opportunities for innovation within the broader engineering project life cycle.
Digital technology has provided Geomatics professionals with new tools that produce new types of data and streamlined delivery channels that can reach an unprecedented number of stakeholders, without the need for those stakeholders to be technical experts in spatial information or have special software and tools. Geomatics professionals, as the creators of this data, remain involved with spatial information long after data is collected in the field. The often large and technical nature of modern Spatial Data also requires a unique set of skills and understanding of the extracted data so that it is leveraged to its fullest extent. The Spatial Data experts in Geomatics have the unique skills required to assist in the processes whereby Spatial Data is transformed into information and intelligence that supports informed decision making throughout the entire project life cycle.
In mapping out the flow of Spatial Data across the engineering project life cycle we can better understand the Spatial Data Value Chain and see how innovation is enabled.
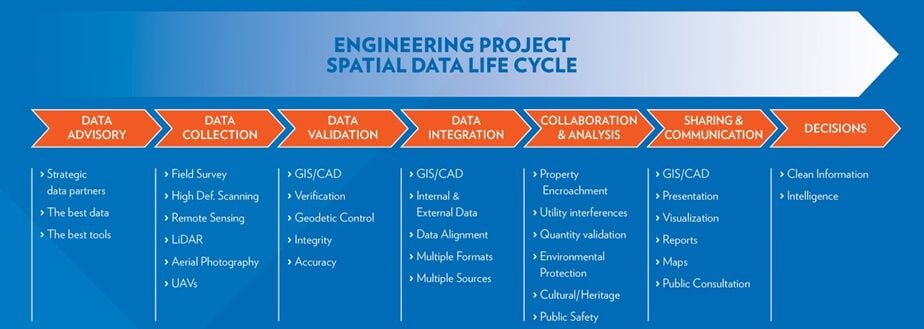
Digital delivery mechanisms like GIS and web portals provide new ways for Spatial Data to be accessed, analyzed and combined with non-spatial information, producing new levels of insight and understanding. In an era where engineering projects face increasing risk mitigation pressure from a multitude of angles (cost overruns, scope creep, timelines, health, safety and the environment), the ability of Geomatics to transform Spatial Data into business intelligence is a valuable resource on all projects.
